Network Topology refers
to layout of a network. How different nodes in a network are
connected to each other and how they communicate is determined by the network's
topology. Network Topology refers to the layout of a network and
how different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they
communicate.
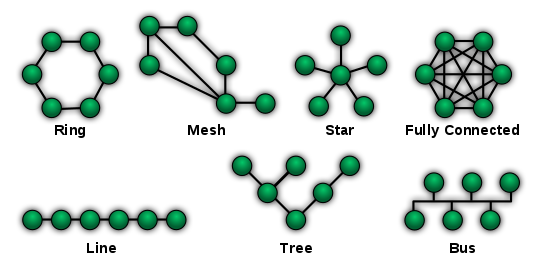
TYPES OF NETWORK TOPOLOGY
1. Bus Topology
 In networking a bus
is the central cable -- the main wire -- that connects all devices on a
local-area network (LAN). It is also called the backbone.
This is often used to describe the main network connections composing the
Internet. Bus networks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for
small networks.
In networking a bus
is the central cable -- the main wire -- that connects all devices on a
local-area network (LAN). It is also called the backbone.
This is often used to describe the main network connections composing the
Internet. Bus networks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install for
small networks.
Main Advantage: It's
easy to connect a computer or device and typically it requires less cable than
a star topology.
Main Disadvantage: The entire network
shuts down if there is a break in the main wire and it can be difficult to
identify the problem if the network shuts down.
2. Star Topology
 In a star network
devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub. Nodes communicate
across the network by passing data through the hub.
In a star network
devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub. Nodes communicate
across the network by passing data through the hub.
Main Advantage: In
a star network, one malfunctioning node doesn't affect the rest of the network.
Main Disadvantage: If the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable.
Main Disadvantage: If the central computer fails, the entire network becomes unusable.
3. Ring Topology
 A local-area network
(LAN) whose topology is a ring. That is, all of the nodes
are connected in a closed loop. Messages travel around the ring, with each node
reading those messages addressed to it.
A local-area network
(LAN) whose topology is a ring. That is, all of the nodes
are connected in a closed loop. Messages travel around the ring, with each node
reading those messages addressed to it. Main Advantage: One main advantage to a ring network is that it can span larger distances than other types of networks, such as bus networks, because each node regenerates messages as they pass through it.
4. Mesh Topology
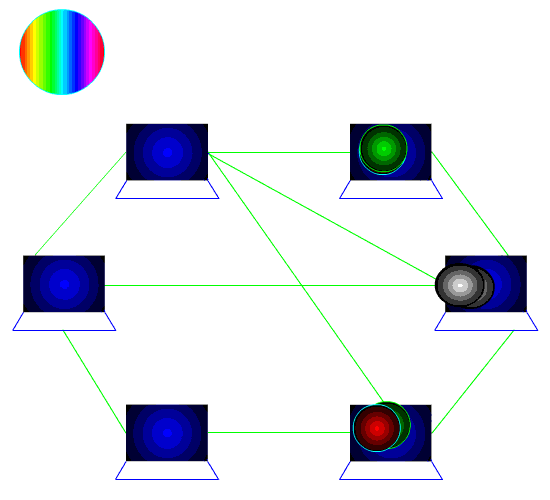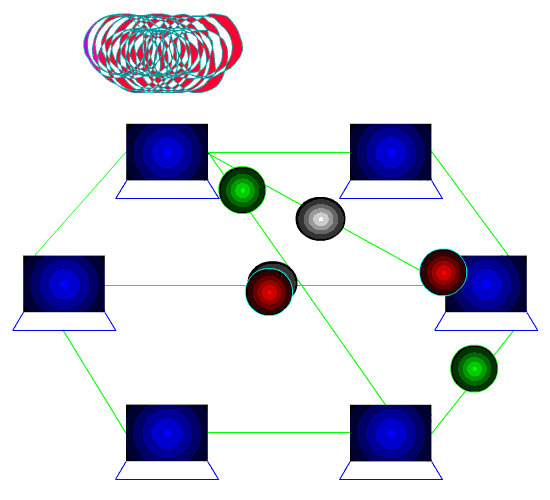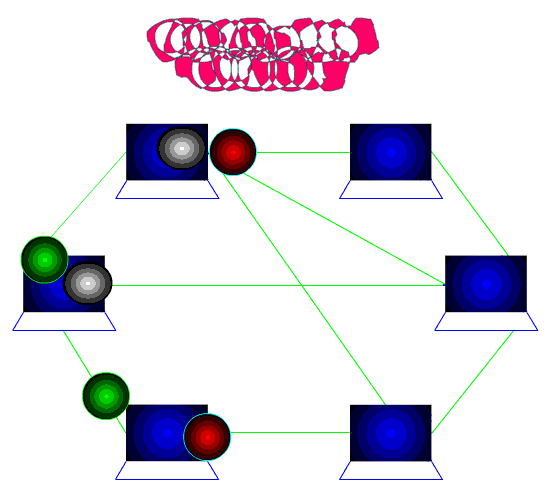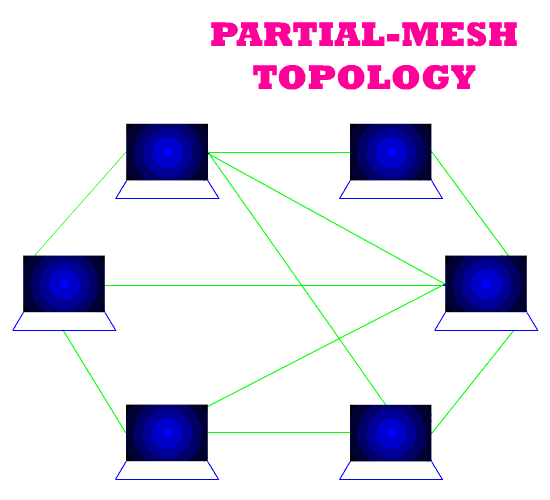 In a mesh network,
devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network
nodes. In a true mesh topology every node has a connection to every other node
in the network. There are two types of mesh topologies:
In a mesh network,
devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network
nodes. In a true mesh topology every node has a connection to every other node
in the network. There are two types of mesh topologies:
Full mesh
topology: occurs when every node has a circuit connecting it to every
other node in a network. Full mesh is very expensive to implement but yields
the greatest amount of redundancy, so in the event that one of those nodes
fails, network traffic can be directed to any of the other nodes. Full mesh is
usually reserved for backbone networks.
Partial mesh topology: is less expensive to implement and yields less redundancy than full mesh topology. With partial mesh, some nodes are organized in a full mesh scheme but others are only connected to one or two in the network. Partial mesh topology is commonly found in peripheral networks connected to a full meshed backbone.
5. Hybrid Topology

A hybrid topology is a type of network topology that uses two or more differing network topologies. These topologies include a mix of bus topology, mesh topology, ring topology, star topology, and tree topology.
Advantages: It is
extremely flexible, very reliable, and easily scalable
Disadvantages: It
is expensive, the design of a hybrid network is complex and hardware changes
are required in order to connect topology to another topology.
No comments:
Post a Comment